Midas Ear (Haliotis midae): A Comprehensive Guide to Its Ecology and Importance
Share

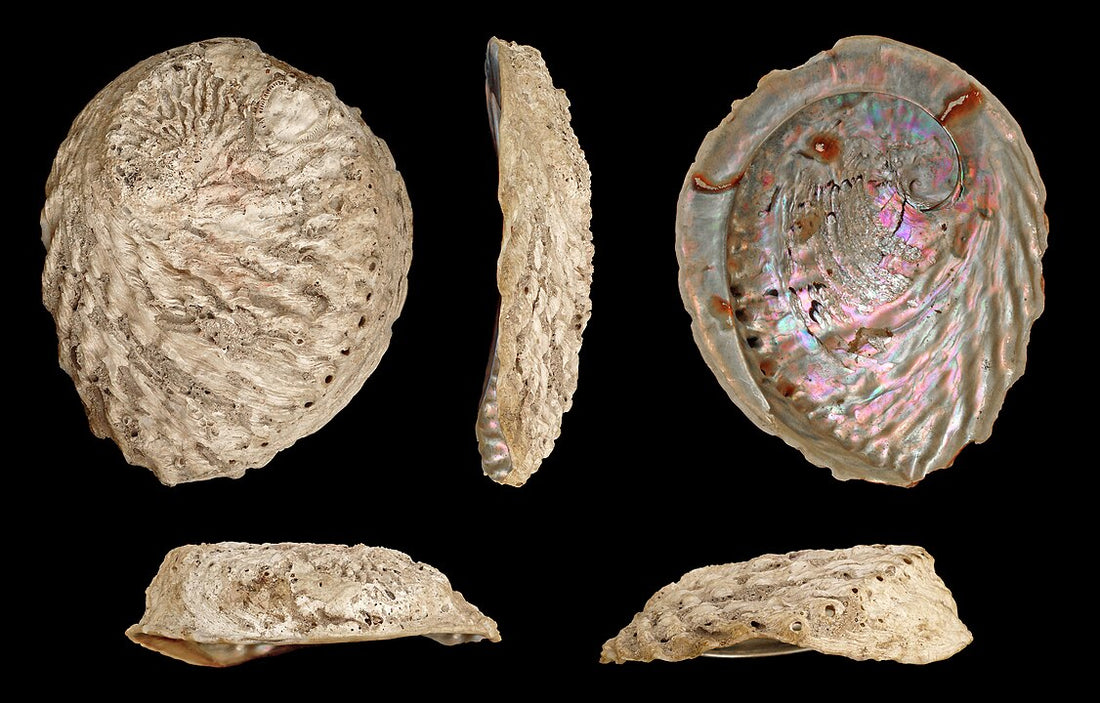
The Midas Ear, scientifically known as Haliotis midae, is a fascinating marine species beloved for its unique characteristics and cultural significance. This large abalone can mature to 234 mm and thrives in shallow waters along the coast of South Africa, making it an important part of the local ecosystem. Its flattened, ear-shaped shell features a distinctive array of small holes, allowing water to escape while keeping the creature's gills aerated.
This species is not just an ecological marvel; it also holds considerable economic weight. Haliotis midae is heavily harvested for its meat and shell, driving both legal and illegal trade. Unfortunately, overfishing has led to a decline in its population, making it a topic of conservation concern.
Readers interested in marine life, culinary applications, or environmental issues will find the story of the Midas Ear both compelling and educational. From its identification to its economic challenges, this article will explore all aspects of this remarkable mollusk.
Key Takeaways
- Haliotis midae can grow up to 234 mm and is found in shallow waters off South Africa.
- This abalone species is economically important but faces threats from overfishing.
- Its shell features small holes for water circulation, distinguishing it from other snail species.
Identification Guide
The Midas Ear, or Haliotis midae, is a large abalone known for its unique features. Identifying this species involves looking at specific physical traits and comparing it to other similar species.
How to Identify a Midas Ear
To identify a Midas Ear, one should focus on its shell shape and surface. The shell is typically oval and can measure between 60 mm to 230 mm in length. The surface often has a glossy appearance with growth lines and ridges.
Another significant feature is the color. Midas Ear usually has shades of green, brown, or grey, which can blend with its rocky habitat. Observing the shell's inner side is also essential. It showcases strong, iridescent colors like blue and green, which are characteristic of this species.
Characteristics
Key characteristics of Haliotis midae include its size and shell structure. The shell has up to 7-9 holes along the edge, which distinguishes it from other types of abalone.
The body of the Midas Ear is fleshy and can be quite large, contributing to its commercial value. This species prefers shallow waters and often seeks shelter under boulders or dense seaweed. Knowing these traits helps in proper identification.
To summarize, key features include:
- Shell shape: Oval
- Size: Up to 234 mm
- Color: Green, brown, or grey with a shiny inner shell
Comparison to Similar Species
Comparing Haliotis midae to similar species is crucial for accurate identification. One similar species is the red abalone (Haliotis rufescens). The red abalone has a more rounded shell and a distinct reddish hue.
Another comparable species is Haliotis discus, which has a flatter shell and different hole placements. Observing the number and arrangement of holes can help differentiate between these species.
A quick comparison chart:
| Feature | Midas Ear (H. midae) | Red Abalone (H. rufescens) | Discus Abalone (H. discus) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shell Shape | Oval | Rounded | Flatter |
| Shell Color | Green, brown, grey | Reddish | Varied shades |
| Hole Count | 7-9 | Fewer, different placement | More evenly spaced |
By focusing on these distinct traits, one can confidently identify and differentiate the Midas Ear from other abalone species.
Distribution & Habitat
Midas Ear, or Haliotis midae, has a specific distribution and habitat that supports its growth and reproduction. This section highlights the key areas where Midas Ear can be found and the environmental conditions that are favorable for its survival.
Where to Find Midas Ear
Midas Ear is primarily found in the Southeast Atlantic, notably along the coast of South Africa. The species thrives in shallow marine environments, typically at depths ranging from 0 to 10 meters.
These snails prefer areas with subtropical waters, ideally at temperatures around 25°C. They often inhabit rocky substrates, where they can attach themselves and access abundant food sources.
The distribution of Midas Ear is patchy, meaning populations may be concentrated in certain locations. Specific regions include the Eastern Cape and other coastal areas, which are crucial for their breeding and growth.
Cultural & Economic Importance
Haliotis midae, known as the Midas Ear or perlemoen, holds significant cultural and economic value, particularly in South Africa. Its status as a delicacy and a symbol in local culture has made it both sought after and heavily regulated.
The Midas Ear in Culture
In South Africa, Midas Ear is more than just food; it is part of the cultural heritage. Many coastal communities value this species for its role in traditional dishes. Abalone is often featured in celebrations and rituals.
Furthermore, the shell of Haliotis midae is prized for its beauty. Artisans craft jewelry and decorative items from the shells, contributing to the local art scene. The connection to cultural identity persists, influencing community pride and traditions.
Legal Status
Due to overexploitation, Haliotis midae is legally protected in South Africa. Fishing regulations are strict, limiting harvest sizes and seasons to prevent population decline. This approach aims to ensure sustainable practices.
The species is listed as vulnerable by the IUCN, highlighting the necessity for conservation efforts. Legal measures include permits for fishing and strict penalties for illegal harvesting. These efforts underscore the balance between cultural significance and economic sustainability.
Midas Ear Crafting
Midas Ear abalone shells are popular in various crafting projects. Their unique appearance makes them attractive for decorative items and jewelry.
Common Craft Uses:
- Jewelry: The vibrant colors and polished surface are ideal for necklaces, earrings, and bracelets.
- Home Decor: They can be used in the creation of wall hangings or centerpieces.
- Art Projects: Crafters use them for mixed-media art or as part of sculptures.
Crafting Tips:
- Polishing: Start with a rough surface and gradually polish using finer grades of sandpaper or polishing compounds.
- Drilling: Use a drill with a small bit to create holes for jewelry, ensuring the shell is securely held.
- Sealing: To protect the sheen, apply a clear sealant after crafting.
Safety Note: When crafting, it's important to source Midas Ear abalone legally. Overharvesting has impacted their populations, and laws may vary by region.
By using these beautiful shells responsibly, crafters can produce stunning items while being mindful of the species’ conservation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Haliotis midae, known as the Midas Ear abalone, has specific features and market conditions that interest many. Understanding its price factors, culinary uses, and farming practices can help anyone interested in this valuable marine species.
What factors determine the price of Haliotis midae?
The price of Haliotis midae is influenced by various factors. These include the size and weight of the abalone, demand in local and international markets, and the legality of its harvest. Additionally, conservation regulations and competition from other seafood can also affect pricing.
How can I identify if Haliotis midae is available for purchase?
To identify the availability of Haliotis midae, one can check local seafood markets and specialty stores that offer marine products. Online seafood retailers may also list this species. Certification from responsible fisheries or aquaculture farms can assure the buyer of its authenticity.
What is the purpose of the respiratory holes in abalone?
Abalone possess respiratory holes, known as siphons, in their shells. These openings allow water to flow over the gills, enabling the abalone to breathe. The holes also facilitate the release of waste materials, helping maintain the creature's health.
How is Haliotis midae referred to in South African culinary context?
In South Africa, Haliotis midae is commonly called "perlemoen." It is considered a delicacy with various culinary uses, often prepared through steaming or grilling. The unique flavor and texture make it highly sought after in local cuisine.
What distinguishes Haliotis midae from other abalone species?
Haliotis midae is unique in its size and distribution, primarily found along the South African coast. It is the largest of the local abalone species and has distinct shell features. The coloration and shell shape can also vary, setting it apart from other types of abalone.
What are the best conditions for farming Haliotis midae?
Farming Haliotis midae requires specific conditions for optimal growth. It thrives in clean, cool waters with good water flow and appropriate food sources, like algae. Proper management of water quality and density of the abalone is crucial to successful farming efforts.